Table of contents
Socialite , my passion project of a social media app, was missing something - the option of real-time interaction! It's time to build a chat feature, and Node.js is our trusty steed. Let's embark on this coding adventure!
The Challenge: Building a fast, real-time chat experience for Socialite's users.
The Weapon: Socket.IO - a powerful library for bi-directional communication between server and client.
The Shield: MongoDB - our reliable data fortress for storing messages and user information.
The Spice: Caching - the secret ingredient for speedy performance!
Setting the Stage:
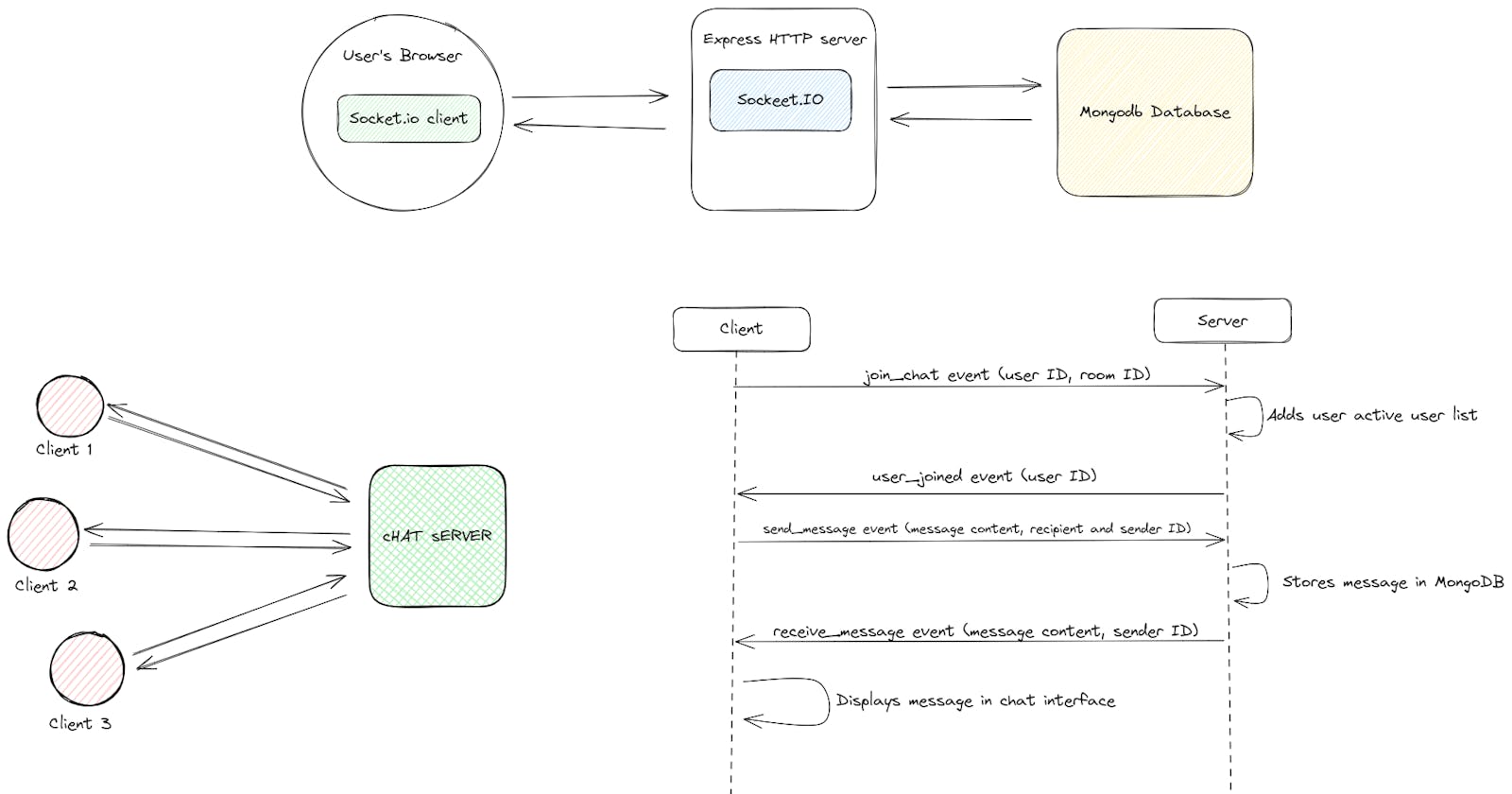
Building the Server: Express.js, our trusty framework, lays the foundation. A Socket.IO server listens for incoming connections and orchestrates the chat symphony.
Connecting the Dots: Clients join chat rooms with their user IDs. We use these IDs to fetch chat history and send messages to the right recipients.
Chat History Cache: Enter the hero, the chat history cache! This in-memory store temporarily holds recently accessed conversations, ensuring lightning-fast retrieval for frequently requested data. Why? MongoDB lookups aren't instant, and frequent database calls can bog things down. The cache acts as a bridge, minimizing those trips and keeping the conversation flowing smoothly.
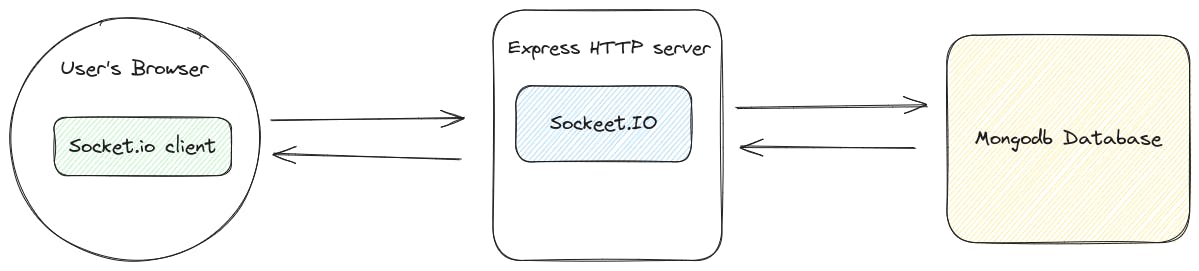
Active Users on the Radar: We keep track of online users using a simple map. When a user joins, they're added to the map, and when they leave, they gracefully exit. This map helps us notify everyone about who's available to chat, keeping the social flame alight.
Message Relay: When a message is sent, First, it's saved in the trusty MongoDB for posterity. Then, it zooms through the network, finding the recipient's connected socket (thanks to the active users map) and delivering the message in real time. No need for constant polling or anxious refreshes - instant gratification, here we come!
Why Caching tho? : Imagine your friends bombarding you with memes right after lunch. Every request would send you running to the fridge. But if you had a snack tray readily available, things would be much smoother, right? That's what the chat history cache does. Frequently accessed messages are readily available in-memory, saving precious database calls and delivering smooth, responsive chat experiences.
Building the Chat Architecture: Event-Driven Architecture and Key Events
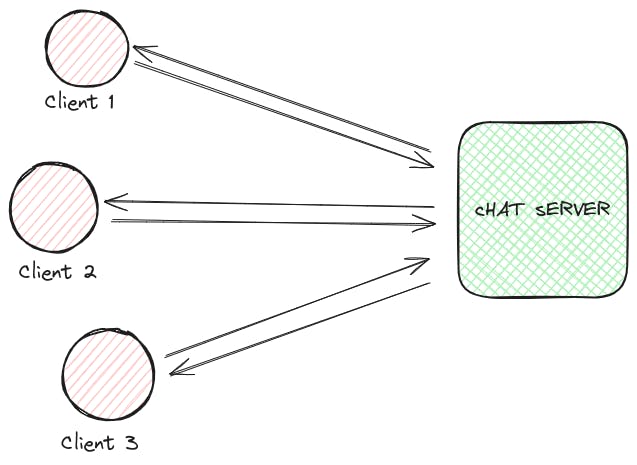
let's dive deeper into the heart of real-time communication: Socket events. These events act as cues for specific actions, orchestrating the flow of information and driving the dynamic chat experience.
Key Events and their Roles:
join_chat: This event fires when a user enters a chat room. The server receives the event, adds the user to the room's participant list, and broadcasts their arrival to all existing participants. This ensures everyone knows who's online and ready to chat.
send_message: When a user types and sends a message, this event triggers. The server captures the message content, sender information, and recipient(s), saves it to MongoDB for permanent storage, and then utilizes Socket.IO to deliver it directly to the intended recipient(s) in real-time.
receive_message: This event acts as the receiver's side of the "send_message" event. When a user receives a message, their browser receives this event, displaying the message on their chat interface, keeping them in the loop of the conversation.
leave_chat: When a user exits a chat room, this event informs the server. The server removes the user from the participant list and broadcasts their departure to other members, ensuring everyone is aware of who's still in the room.
typing_indicator: This optional event can be implemented to provide real-time typing feedback. When a user starts typing, a "typing_indicator" event can be emitted, notifying other participants in the room that they can expect a message soon.
These are just some core events in Socialite's chat architecture. Depending on your specific needs, you can implement additional events to handle group chats, private messages, notifications, and other features.
Benefits of Event-Driven Architecture:
Responsiveness: Events allow for immediate reactions to user actions, leading to a more responsive and fluid chat experience.
Decoupling: Events decouple components of the chat system, making them more modular and easier to maintain.
Scalability: Event-driven architecture can handle increased traffic and workload more efficiently than traditional request-response models.
Considerations for Event Design:
Event naming: Choose descriptive and consistent event names for clarity and ease of understanding.
Event parameters: Use parameters to pass relevant information within an event, ensuring the server has the necessary data to react appropriately.
Error handling: Implement robust error handling for event transmission and processing to ensure smooth operation.
Time To Code! Diving into the Server-Side
It's time to venture into the engine room of Socialite's chat feature and witness the code that makes real-time conversations possible. We'll dive into the server-side implementation, exploring key functions and how they coordinate to bring messages to life.
Setting the Stage: Server Setup
import express from "express";
import mongoose from "mongoose";
import cors from "cors";
import dotenv from "dotenv";
import { createServer } from "node:http";
import { Server } from "socket.io";
import {
handleChatConnection,
setIoInstance,
} from "./controllers/chatController.js";
dotenv.config();
const app = express();
const server = createServer(app);
const io = new Server(server);
app.use(cors());
// Set Socket.IO instance
setIoInstance(io);
// Chat connection handling
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
handleChatConnection(socket);
});
// Mongoose connection
mongoose
.connect(process.env.MONGO_URL, {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true,
})
.then(() => {
server.listen(process.env.PORT || 3001, () => console.log("Server running"));
})
.catch((error) => console.log(error.message));
Imports: Imports necessary libraries for server setup, middleware, and chat functionality.
Configs: Loads environment variables using
dotenv.App instance: Creates an Express app instance.
Server and Socket.IO: Creates an HTTP server and a Socket.IO instance for real-time communication.
Middleware: Uses CORS middleware to enable cross-origin requests.
-
Sets the Socket.IO instance using
setIoInstance.Listens for new connections and handles them using
handleChatConnection.
Mongoose connection:
Connects to MongoDB using Mongoose.
Starts the server after a successful connection.
Setting up the Store: The Message Model
import mongoose from "mongoose";
const messageSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
senderId: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User', required: true },
recipientId: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User', required: true },
message: { type: String, required: true },
createdAt: { type: Date, default: Date.now },
});
const Message = mongoose.model('Message', messageSchema);
export default Message;
Import Mongoose: Brings in the Mongoose library for interacting with MongoDB.
Define Message Schema: Creates a schema that outlines the structure of each message document:
senderId: The MongoDB ObjectId of the message sender, referencing a user in the User collection.recipientId: The MongoDB ObjectId of the message recipient, also referencing a user.message: The text content of the message.createdAt: The timestamp when the message was created, automatically set to the current date and time.
Export Message Model: Exports the Mongoose model named
Message, making it available for use in other parts of the application.
Note:
Relationships: The
refproperty insenderIdandrecipientIdestablishes links to the User collection, enabling efficient retrieval of user information alongside messages.Timestamps: The
createdAtfield facilitates chronological ordering of messages and potential time-based features like message history viewing and sorting.
Orchestrating Connections and Conversations: The Chat Controller
Now, let's venture into the heart of the chat functionality, where connections are established, messages are exchanged, and users gracefully depart. The chat controller expertly directs this symphony of real-time interactions:
import Message from "./../models/Message.js";
const activeUsers = new Map(); // Stores active user sockets and IDs
const chatHistoryCache = new Map(); // Caches chat history for performance
let ioInstance; // Holds the Socket.IO instance for use in functions
// Sets the Socket.IO instance for use within the controller
export const setIoInstance = (io) => {
ioInstance = io;
};
// Handles incoming chat connections
export const handleChatConnection = (socket) => {
console.log(`Socket connected: ${socket.id}`);
// Join chat room and emit chat history
socket.on("join_chat", async ({ userId }) => {
try {
socket.join(userId); // Joins the chat room with the user's ID
// Check cache first for chat history
const cachedHistory = chatHistoryCache.get(userId);
if (cachedHistory) {
socket.emit("chat_history", cachedHistory);
} else {
// Fetch chat history from database if not cached
const chatHistory = await Message.find({
$or: [{ senderId: userId }, { recipientId: userId }],
}).sort({ createdAt: "asc" });
socket.emit("chat_history", chatHistory);
chatHistoryCache.set(userId, chatHistory); // Update cache
}
// Add user to active users map and emit updated list
activeUsers.set(socket.id, { userId, socket });
ioInstance.emit(
"active_users",
[...activeUsers.values()].map((user) => user.userId)
);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error joining chat:", error);
}
});
// Handles incoming messages
socket.on("send_message", async ({ senderId, recipientId, message }) => {
try {
// Create a new message in the database
const newMessage = await Message.create({
senderId,
recipientId,
message,
});
// Find recipient's socket if online and emit message directly
const recipientSocket = [...activeUsers.values()].find(
(user) => user.userId === recipientId
)?.socket;
if (recipientSocket) {
recipientSocket.emit("receive_message", {
senderId,
message: newMessage.message,
createdAt: newMessage.createdAt,
});
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error creating message:", error);
}
});
// Handles socket disconnections
socket.on("disconnect", () => {
console.log(`Socket disconnected: ${socket.id}`);
activeUsers.delete(socket.id); // Remove user from active users map
// Emit updated list of active users
ioInstance.emit(
"active_users",
[...activeUsers.values()].map((user) => user.userId)
);
});
};
Functional Breakdown:
- setIoInstance:
Purpose: Sets the shared Socket.IO instance, ensuring consistent communication across functions.
Context: Used to establish a common reference to the Socket.IO server for broadcasting events and managing connections.
Benefits:
Avoids potential errors caused by using different Socket.IO instances.
Facilitates seamless coordination of real-time events.
- handleChatConnection:
Purpose: Manages incoming chat connections, handling events and coordinating data flow.
Key Events:
"join_chat":
Joins the socket to a chat room using
socket.join(userId), enabling targeted communication within specific conversations.Efficiently retrieves chat history using a caching mechanism:
Checks the
chatHistoryCachefor quick retrieval.Fetches from the database using
Message.findif not cached, optimizing database interactions.
Updates the
activeUsersmap for tracking online users and emits an updated list to all clients usingioInstance.emit("active_users", ...), ensuring real-time visibility of online presence.
"send_message":
Persists messages in the database using
Message.create, ensuring data consistency and enabling retrieval for later viewing.Prioritizes real-time delivery by directly emitting messages to the recipient's socket if they're online, providing instant communication experiences.
"disconnect":
- Gracefully handles socket disconnections by removing the user from the
activeUsersmap and emitting an updated list, maintaining accurate online presence information for all clients.
- Gracefully handles socket disconnections by removing the user from the
Insights:
Data Structures:
activeUsersmap: Efficiently tracks active sockets and user IDs for targeted message delivery and presence management.chatHistoryCache: Optimizes chat history retrieval, reducing database load and enhancing performance.
Error Handling:
- Uses
try...catchblocks to handle potential errors during database operations and chat events, ensuring graceful error management and preventing application crashes.
- Uses
Modularity:
- Encapsulates chat functionality within a controller file, promoting code organization and maintainability.
Considerations for the Road Ahead: Embracing Technology for Scalable Growth
As our chat platform welcomes more users and their conversations, keeping pace with growth demands strategic choices. Let's delve into the tools and technologies that can empower our chat experience, ensuring scalability, performance, and a thriving community:
Redis: A Cache Champion for Enhanced Performance:
Move beyond in-memory caching with Redis, a powerful in-memory data store built for performance and scalability. Here's how it can be your ally:
Chat History Caching: Cache frequently accessed user chat history in Redis, minimizing database load and delivering lightning-fast retrieval times.
Active User List: Keep track of online users in Redis, enabling instant presence updates and optimizing targeted broadcasts.
Pub/Sub, Whispering Messages in Real-Time: Picture new messages seamlessly reaching their recipients without delay. Redis Pub/Sub makes this magic happen. Imagine publishing a message to a channel, and all subscribed clients (those currently in a conversation) receive it instantly, bypassing unnecessary server interactions. Real-time conversations flow like a sparkling stream, without a hitch.
Load Balancing and Server Scaling:
As your user base grows, prepare for increased traffic by distributing the load across multiple servers using load balancers.
Cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud offer managed load balancing services, simplifying configuration and scaling.
Consider horizontal scaling by adding more servers to handle increased traffic, ensuring responsiveness and smooth performance.
CI/CD: Automation fuels Innovation:
Imagine new features seamlessly joining the conversation, polished and ready to impress. This is the magic of continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
CI/CD automates code compilation, testing, and deployment, accelerating development cycles and reducing errors. With new features flowing like refreshing drinks, our celebration keeps evolving, always exciting and engaging.
Microservices: Modularity for a Scalability :
As our user base flourishes, imagine dividing the application into smaller, independent musicians, each playing a specific tune – user management, chat history, and message delivery. This is the beauty of microservices architecture.
Each microservice focuses on its own task, making the code easier to maintain and scale. If one instrument needs more volume (resources), we can amplify it without affecting the others
From Code to Conversation: Key Takeaways
Our journey of building a real-time chat application in Node.js leaves us with insights and a blueprint for crafting engaging communication platforms. Here are the key takeaways to keep in your developer's toolbox:
1. Embrace the Power of Real-Time: Node.js shines in orchestrating real-time communication, enabling instant message delivery and dynamic presence updates. Witnessing conversations unfold in real-time adds an undeniable spark to the user experience.
2. Structure Matters: A well-defined message schema and efficient data structures like active user maps and chat history caches lay the foundation for performance and scalability. Remember, organized data is happy data!
3. Listen and Respond: Socket.IO empowers responsive interactions, allowing clients to join chat rooms, send and receive messages, and gracefully disconnect. The more you listen to user actions, the more seamless the conversation becomes.
4. Technology as Your Ally: Don't shy away from leveraging technologies like Redis for caching and Pub/Sub for real-time messaging. Microservices architecture and load balancing can further pave the way for a scalable and robust platform.
5. Security First: Building trust is crucial. Implement robust authentication, authorization, and data encryption to ensure a safe and secure environment for your users' conversations.
Now it's your turn!
Adapt and Evolve: Take these insights and tailor them to your specific project. Every chat platform has its own unique story to tell.
Share Your Voice: Let us know in the comments below what resonated with you most. Did you find any particular aspect of the code or concepts especially insightful?
Explore Further: This is just the beginning! Dive deeper into Node.js real-time capabilities, explore libraries like Socket.io , redis, Kafka etc and keep your creativity flowing.
Remember, building a thriving chat application is an ongoing conversation. By embracing the power of technology, prioritizing user experience, and constantly seeking new solutions, you can create a platform where connections blossom and ideas take flight. So, keep coding, keep learning, and keep the conversations flowing!